Understanding Sperm Donor Qualifications: What You Need to Know
Becoming a sperm donor is a significant decision that impacts not only your life but potentially the lives of countless families seeking to fulfill their dreams of parenthood. Understanding the qualifications required is essential for anyone considering this path.
The selection process ensures both donor and recipient safety while maintaining the highest standards in reproductive medicine.
Key Takeaways
- Age requirements are always in place, with sperm banks typically accepting donors between 18-38 years old to ensure optimal sperm quality and minimize genetic risks associated with advanced paternal age.
- Comprehensive genetic screening has become standard practice, with leading banks testing 100% of donors for at least 266 genetic conditions to protect the health of potential children.
- Educational background significantly impacts acceptance rates, as research shows only 2.3% of U.S. sperm donors had only a high school diploma, reflecting recipient preferences for donors with higher education.
- Qualified donors can earn substantial compensation, ranging from $1,000-$1,400 monthly, while receiving valuable benefits including free comprehensive health screenings and genetic testing worth over $2,000.
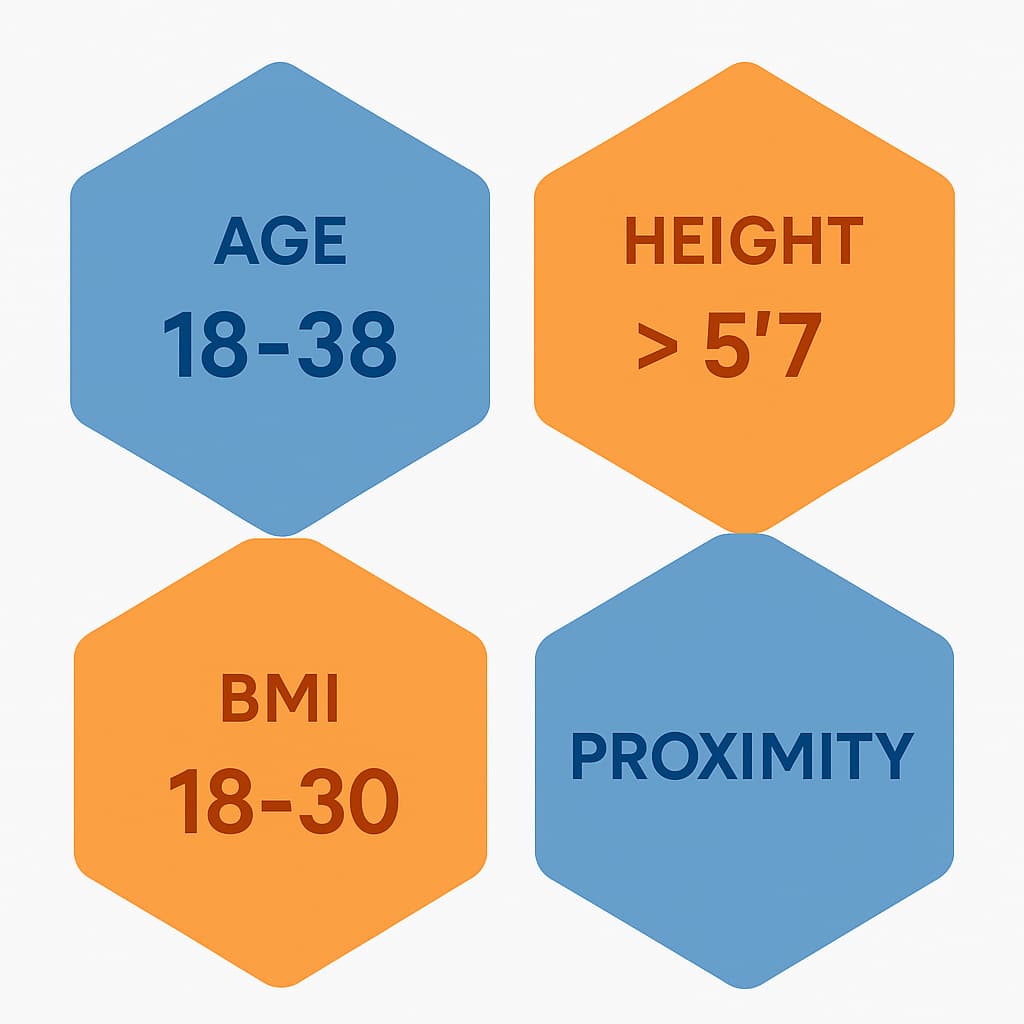
Age and Physical Requirements (Ages 18-38)

Age represents one of the most fundamental qualification factors for sperm donors. Donors typically must be between 18 and 38 years old (This is the case at our sperm donation center, Donatesperm.com). This range isn’t arbitrary – it’s carefully established to ensure optimal sperm quality while minimizing risks associated with advanced paternal age, with most sperm banks having a similar age requirement for donation.
Our age requirement of 18-38 years old aligns with industry standards that prioritize reproductive health based on age parameters. This requirement reflects current research on sperm quality and genetic stability across different age groups.
Beyond age requirements, physical qualifications typically include:
- Healthy BMI (typically between 18-30)
- Minimum height requirements (many banks prefer donors over 5’7″)
- No recent tattoos or piercings (usually within the past 12 months)
- Good overall physical health
- Residence within a reasonable distance of a donation center
These physical criteria help ensure donors are in optimal health, which correlates with sperm quality and genetic health outcomes for potential offspring. For individuals preparing for their first donation appointment, understanding these baseline qualifications can help set appropriate expectations.
Medical and Genetic Screening Protocols
Modern sperm donation programs implement extraordinarily thorough medical and genetic screening protocols. This comprehensive approach is necessary to protect the health of potential children and provide peace of mind to recipient families.
Genetic Testing
The standard for genetic screening has risen dramatically in recent years. 100% of donors at leading banks undergo carrier screening for at least 266 genetic conditions. This extensive testing helps identify carriers of inheritable diseases, allowing for informed decisions by recipient families.
The American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) has played a crucial role in establishing these standards. Facing the challenge of creating consistent, evidence-based protocols across the country, ASRM published updated 2024 guidance that includes comprehensive medical and sexual history reviews, physical examinations, laboratory and genetic testing, and psychological evaluations—all integrated into a uniform framework for donor eligibility. This standardized approach has provided consistent, nationwide protocols that improve donor safety, optimize offspring health, and ensure adherence to FDA and industry standards.
Infectious Disease Testing
In addition to genetic screening, donors undergo regular testing for infectious diseases, including:
- HIV 1 and 2
- Hepatitis B and C
- HTLV I and II
- Syphilis
- Chlamydia
- Gonorrhea
- CMV (cytomegalovirus)
These tests are typically repeated every three months during the donation period to ensure continued safety and compliance with FDA regulations.
Genetic Research Advancements
Advanced genetic research continues to improve donor screening methods. The Hunan Province Human Sperm Bank of China addressed concerns regarding the accuracy and consistency of genetic screening by conducting comparative genetic analysis using exome sequencing on paired blood and semen samples from 40 donors. Their research identified 108 pathogenic/likely pathogenic variants with an average of 2.7 variants per donor and demonstrated near-total consistency between blood and semen samples. This innovative approach has helped streamline the genetic screening process while enhancing confidence in the genetic quality of selected donors.
Educational and Demographic Considerations
Educational Requirements
Education level has emerged as a significant qualifying factor at many sperm banks. According to research published in Fertility and Sterility, only 2.3% of U.S. sperm donors had only a high school diploma, indicating a strong preference for higher education among accepted donors.
This preference reflects both market demand and strategic considerations by sperm banks. Many recipient families specifically request donors with college degrees or graduate education, making these donors particularly valuable to sperm banks. However, some facilities have begun accepting candidates with high school diplomas and trade certifications, recognizing the importance of skills and practical expertise alongside traditional academic achievements.
DonateSperm.com typically looks for donors who are either enrolled in or have completed college education, though exceptions may be made for candidates with exceptional qualities in other areas.
Demographics and Diversity
Diversity remains a challenge in sperm donation. According to the Human Fertilisation and Embryology Authority (HFEA), 87% of UK sperm donors registered from 2016–2020 were White, with only 2% Black and 7% Asian. This demographic imbalance highlights the need for increased recruitment from underrepresented groups.
Many sperm banks, including DonateSperm.com, are actively working to address this disparity by implementing targeted recruitment campaigns for donors from diverse ethnic backgrounds. This effort serves the growing demand from families seeking donors who share their cultural or ethnic heritage, allowing children to connect with their genetic origins more meaningfully.
The Donor Screening Process
The journey from application to becoming an approved sperm donor involves multiple steps designed to thoroughly evaluate candidates. Understanding this process helps potential donors know what to expect and how to prepare for each stage.
Initial Application and Interview
The process begins with an online application that typically includes basic biographical information, medical history, and family health background. Candidates who pass this initial screening are invited for an in-person interview and preliminary testing.
Sperm Bank, Inc. in California has refined this process to balance thoroughness with efficiency. Facing the challenge of attracting a consistent pool of highly qualified sperm donors while maintaining rigorous health and genetic screening protocols despite increasing industry demand, they implemented strict qualification criteria including age limits (18–38), college education, detailed health and genetic history, regular medical testing, and robust compensation schemes. This approach successfully increased donor retention and program commitment, ensuring high-quality donor sperm and resulting in improved outcomes for recipient families.
Semen Analysis
A critical component of qualification is semen analysis, which evaluates:
- Sperm count (concentration)
- Motility (movement)
- Morphology (shape)
- Post-thaw recovery (how well sperm survives freezing)
Most importantly, donors must have sperm that performs well after the freezing and thawing process, as all donated samples are cryopreserved before use. This requirement alone eliminates a significant percentage of otherwise healthy candidates, contributing to the selective nature of sperm donor qualifications.
Psychological Evaluation
Psychological screening is another vital component of the qualification process. This evaluation typically includes:
- Standardized psychological tests
- In-depth interviews about motivation and expectations
- Assessment of emotional stability and maturity
- Evaluation of comfort with the long-term implications of donation
This step ensures that donors fully understand the commitment and potential future impact of their decision to donate, debunking common myths about sperm donation that might lead to misconceptions.
Ethical and Privacy Standards
Ethical considerations and privacy protections are fundamental aspects of sperm donor programs. As The World Egg and Sperm Bank (WESB) has demonstrated, ensuring that donors meet not only rigorous health and genetic standards but also ethical and privacy requirements is essential in today’s regulatory environment.
WESB developed a comprehensive screening protocol that integrates strict age limits, family and personal medical history reviews, mandatory genetic and infectious disease testing, and behavioral assessments. Their process accepts less than 5% of applicants, thereby maintaining very high standards. This approach has enhanced both donor safety and recipient trust through rigorous screening while safeguarding donor privacy and ensuring ethical transparency.
Key ethical and privacy standards include:
- Informed consent procedures for donors
- Clear policies on donor anonymity vs. identity release
- Secure handling of personal and genetic information
- Limits on the number of families created from a single donor
- Protocols for updating medical information over time
Many sperm banks now offer tiered options for donor privacy, ranging from completely anonymous donation to “ID release” programs where donors agree to potential contact from offspring after they reach adulthood.
Compensation and Benefits
While altruism often motivates sperm donors, compensation remains an important consideration. Most U.S. sperm banks offer competitive compensation, typically between $100-$150 per approved donation, with potential monthly earnings ranging from $1,000 to $1,400 for regular donors.
At DonateSperm.com, donors can earn up to $1,400 per month, with additional referral bonuses available. This compensation reflects both the time commitment required and the value placed on qualified donors who meet all screening criteria.
Beyond financial compensation, donors typically receive additional benefits, including:
- Free comprehensive health screenings and physical exams
- Detailed genetic testing (a $2,000+ value)
- Regular STI testing
- Medical insights about personal health and fertility
These benefits provide tangible value beyond monetary compensation and often attract donors interested in monitoring their health while helping others.
Evolving Sperm Donor Qualification Standards
As genetic testing capabilities advance, qualification standards are likely to become even more sophisticated. Future screening may include:
- Expanded carrier testing for additional rare genetic conditions
- Epigenetic screening to assess heritable non-genetic factors
- More advanced sperm function tests to predict IVF success rates
- Comprehensive psychological assessments using validated tools
These advances will further refine the selection process, potentially leading to even higher success rates while maintaining safety for all parties involved in assisted reproduction.
Conclusion
Becoming a sperm donor involves meeting rigorous qualifications designed to ensure the health and well-being of all parties involved. From age and physical requirements to comprehensive genetic screening and psychological evaluation, these standards reflect the serious responsibility of helping create new lives.
The sperm donor qualifications set by sperm banks like us at DonateSperm.com serve an essential purpose: ensuring the highest standards of safety, genetic health, and ethical practice. For those considering donation, understanding these qualifications is the first step in determining eligibility and making an informed decision.
Whether motivated by compensation, altruism, or both, qualified sperm donors play a vital role in helping individuals and couples achieve their dreams of parenthood. By maintaining high standards for donor qualifications, sperm banks ensure that recipient families receive the highest quality care while protecting the interests of donors and future offspring alike.
If you’re considering becoming a sperm donor and meet the qualifications outlined above, you can Donate Sperm Today at One of Our Locations across Georgia and North Carolina. At Donatesperm.com, the process begins with a simple online application, followed by an in-person screening appointment at your nearest donation center. Apply today!
